
|
For all your safety sign needsOpen till late - 0208 133 6709 |
| Class 1 Explosives | |||
| sub class | symbol | Description | Examples |
 |
These materials will explode | Pyrotechnics Fireworks TNT Nitro-glycerine |
|
| Class 2 Gases | |||
| sub class | symbol | Description | Examples |
| 2.1 Flammable Gases |  |
These are gases which will burn | Propane Butane Acetylene Hydrogen LPG |
| Class 2.2 Non-flammable Non-toxic gases |
 |
These gases are usually compressed and so are a source of stored energy and some may also present an anoxic hazard (that is, they will exclude oxygen and so kill through asphyxiation). These containers may rocket if valves are damaged or containers are involved in a fire. | Oxygen
Air Carbon dioxide Nitrogen |
| Class 2.3 Toxic Gas | 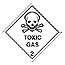 |
These gases are toxic. Being gases they will rapidly disperse if there is a leak. This may reduce the concentration and the hazard, but it will also spread the gas further, so increasing the risk of poisoning people. | Chlorine Methyl Bromide Nitric Acid |
| Class 3 Flammable Liquids | |||
| sub class | symbol | Description | Examples |
 |
These liquids will burn. | Petrol Alcohol Paraffin |
|
| Class 4 Flammable Solids | |||
| sub class | symbol | Description | Examples |
| Class 4.1 Flammable solids self- reactive and related substances and desensitised explosives |
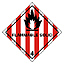 |
Solids easily ignited and readily combustible. These are ordinarily flammable solids which don't fit into Class 4.2 or 4.3 | Sulphur Phosphorus Picric Acid |
| Class 4.2 Spontaneously combustible |  |
The materials will catch fire if exposed to air without any heat being applied (that is, the heat from the normal air is sufficient for them to catch fire - no other source of heat is required). | Charcoal (non-activated) |
| Class 4.3 Dangerous when wet |  |
This class is also know as 'Emits flammable gases when wet'. This class has a particular hazard: not only can moisture from the air cause a fire, but if water or foam is used to extinguish them, it will make the situation worse. | Calcium Carbide |
| Class 5 Oxidising substances | |||
| sub class | symbol | Description | Examples |
| Class 5.1 Oxidising agent |
 |
These are all oxidising agents other than organic peroxides. When substances burn in air, they combine with oxygen and so are said to have been oxidised. Other chemicals have a similar 'burning' effect and so are said to be oxidising agents. The largest group of these are organic peroxides | Chlorine Calcium Hypochlorite Sodium Peroxide |
| Class 5.2 Organic peroxides (liquid or solid) |
 |
These are a particular class of oxidising agent. They have all the normal hazards of oxidising agents (that is, they will cause a 'chemical burning'). In addition, they will often be explosive under certain conditions - especially, if they are allowed to dry out | Benzoyl Peroxides Methyl ethyl Ketone peroxides (MEKP) |
| Class 6 Poisonous & infectious substances | |||
| sub class | symbol | Description | Examples |
| Class 6.1a Toxic |  |
These are liable to cause death or serious injury to human health if inhaled, swallowed or absorbed through the skin. They are covered by special regulations and need special recognition. | Cyanides Lead Arsenic |
| Class 6.1b Harmful | 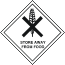 |
These materials which must be stored away from food stuffs but which are not classified as poisons. | Pesticides Heavy Metals |
| Class 6.2 Infectious Substances |
 |
Substances containing viable micro-organisms that may cause disease in humans or animals | Diagnostic specimens or live vaccines |
| Class 7 Radioactive substances | |||
| sub class | symbol | Description | Examples |
 |
Materials or combinations of materials which spontaneously emit ionising radiation. | Uranium Radio Isotopes Plutonium |
|
| Class 8 Corrosives | |||
| sub class | symbol | Description | Examples |
 |
These chemicals will eat away at a wide range of materials including some materials of construction for tanks and probably your eyes and skin. Care must be taken to ensure the containers and packages are made from the right materials and the chemicals do not contact your clothes, skin or eyes. Special protective equipment needs to be worn. | Hydrochloric
acid Sodium Hypochlorite (liquid pool chlorine) Sodium Hydroxide (caustic soda) |
|
| Class 9 Miscellaneous Goods | |||
| sub class | symbol | Description | Examples |
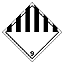 |
Substances and articles which have potentially dangerous properties that are relatively minor, or are not covered by any of the classes already described | Aerosols Polyester beads |
|
 Safety Signs - Owned and Operated by BCW Office Products LTD registration 05693956, VAT 900 3466 61.
Safety Signs - Owned and Operated by BCW Office Products LTD registration 05693956, VAT 900 3466 61.
(c) 2017 BCW. Website design Crawshay Gallery / Number 6 Consulting LLC All rights reserved.